In an age where technology advances at breakneck speed, IoT and 5G have taken businesses into an era of unprecedented connectivity and efficiency. However, with this seamless integration of devices and the lightning-fast speed comes an equally powerful surge in cybersecurity threats.
As businesses embrace the limitless potential of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the transformative power of 5G networks, they also open themselves to the vectors of vulnerabilities. The question isn’t whether businesses should embrace IoT and 5G but how to navigate this landscape securely.
This blog post delves into the heart of the matter, unveiling strategies that empower businesses to harness the benefits of IoT and 5G without compromising security.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Cybersecurity Threats Posed by IoT & 5G
As per Astra, every day witnesses 2,200 cyber attacks, occurring every 39 seconds on average. A data breach costs around $9.44M in the US, contributing to a projected $8 trillion global cybercrime cost by 2023.
These alarming statistics highlight the escalating threat of cyberattacks in today’s digital landscape.
With the rise of IoT devices and the upcoming deployment of 5G networks, the attack surface for cybercriminals is expanding rapidly.
One of the leading cybersecurity threats posed by IoT and 5G is the increased vulnerability of connected devices. IoT devices, like smart home appliances, industrial sensors, and wearables, are often not designed with robust security features.
It makes them easy targets for hackers who can exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or control over these devices.
Furthermore, the high-speed and low-latency nature of 5G networks opens up new possibilities for cyberattacks.
For example, hackers can launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks at an unprecedented scale, overwhelming network resources and disrupting critical services.
Additionally, the increased number of devices connected to the network increases the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
Also Read: Riding 5G Wave: Opportunities and Challenges for High-Speed Mobile App Development
Data Breach & Recent Incidents
And then there is the haunting specter of data breaches. With all these devices interconnected, a breach in one can open a gateway to the entire network.
Remember the Mirai botnet attack?
It turned IoT devices into an army of attackers, disrupting major online services. Also, the recent wave of ransomware attacks targeting healthcare organizations serves as stark reminders of the cybersecurity risks posed by IoT and 5G.
Importance of Securing IoT Devices
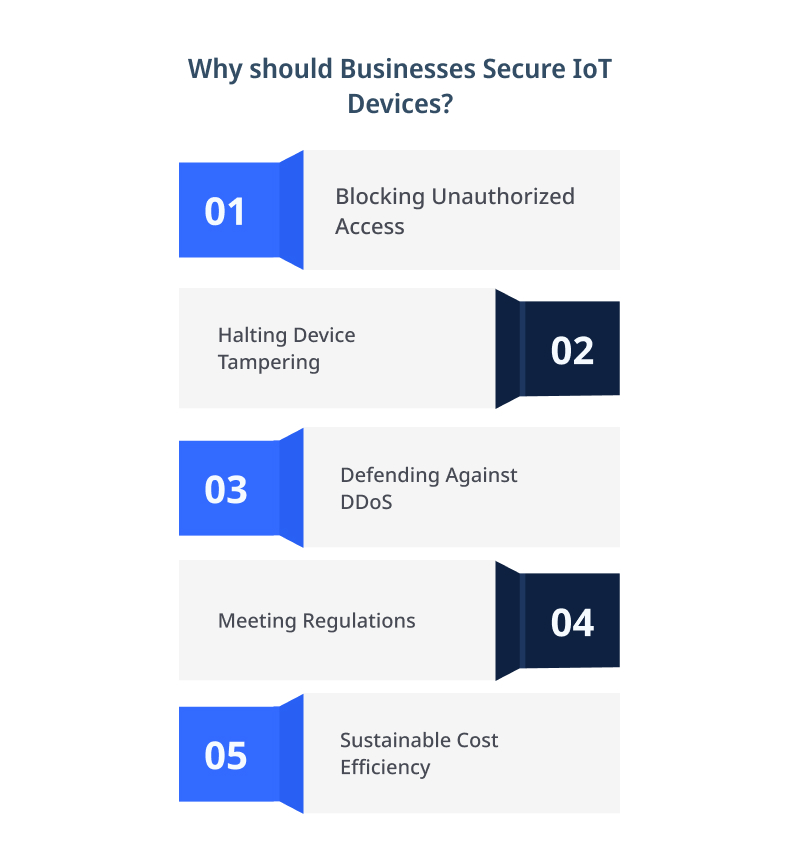
Neglecting the security of IoT devices can have severe consequences for individuals and businesses. Here are a few key reasons why securing IoT devices should be a top priority:
Protection Against Unauthorized Access
IoT devices often gather and transmit sensitive data. Failing to secure these devices leaves them vulnerable to unauthorized access, putting personal and confidential information at risk.
By implementing robust security measures, like strong authentication protocols and encryption, businesses can protect sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands.
Prevention of Device Manipulation
Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices to access control over them. It can have serious consequences, especially in critical infrastructures or industrial settings.
By securing IoT devices, businesses can prevent unauthorized manipulation and maintain the integrity of their operations.
Safeguarding Against DDoS Attacks
Cybercriminals can harness insecure IoT devices to launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. These attacks overwhelm network resources and can disrupt critical services.
By securing IoT devices and ensuring they are not easily compromised, businesses can help prevent such attacks and maintain the availability of their networks.
Compliance with Regulations
Many industries have specific regulations in place regarding the security of IoT devices.
Failing to secure these devices can result in non-compliance, leading to potential legal and financial consequences. By prioritizing IoT device security, businesses can ensure they meet the necessary regulatory requirements.
Also Read: Addressing Legal and Regulatory Compliance in App Development: A Guide for Developers
Long-term Cost Savings
Investing in IoT device security upfront can lead to long-term cost savings. The potential financial impact of a data breach or cyberattack far exceeds the investment required to implement proper security measures.
By taking proactive steps to secure IoT devices, businesses can save themselves from significant financial losses in the future.
Challenges in Securing IoT Devices
According to Payments Cards & Mobile, 90% of businesses are deploying IoT devices, but only 10% are confident in the security measures protecting these devices. It highlights the challenges businesses face in securing IoT devices.
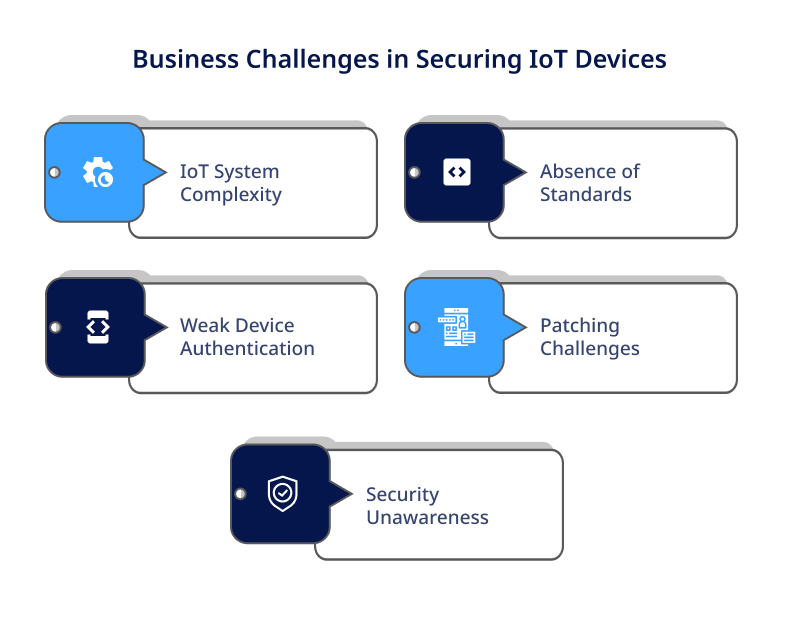
Complexity of IoT ecosystems
IoT ecosystems are complex, consisting of various devices, sensors, and platforms interconnected through networks. Each component in the ecosystem introduces potential vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit.
Securing such a diverse and interconnected environment is a challenge, as organizations must consider the security of every device and the entire network.
Lack of Standardization
The lack of standardization in IoT device security protocols and frameworks makes it difficult to ensure consistent and robust security measures.
With many IoT devices from different manufacturers operating on various platforms, businesses struggle to implement uniform security practices across their IoT ecosystem.
Inadequate Device Authentication
Many IoT devices have weak or no authentication mechanisms, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access. Passwords are often the only form of authentication, and these are frequently not changed from default settings or are easily guessable.
Without proper device authentication, businesses cannot ensure the integrity and security of their IoT devices.
Patch Management
IoT devices often lack a built-in capability to receive and install security patches.
As a result, businesses face challenges in keeping their IoT devices up-to-date with the latest security fixes. It can leave devices exposed to known vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit.
Lack of Security Awareness
Many organizations and individuals lack awareness about the cybersecurity risks associated with IoT devices. This lack of knowledge leads to negligence in implementing proper security measures.
Employees may not be trained to recognize and respond to potential threats, making them unwittingly vulnerable to social engineering attacks or unintentionally introducing malware into the network.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices
Securing IoT devices is crucial for businesses looking to protect their data and networks from cyber threats. Here are some best practices to consider when it comes to securing IoT devices:
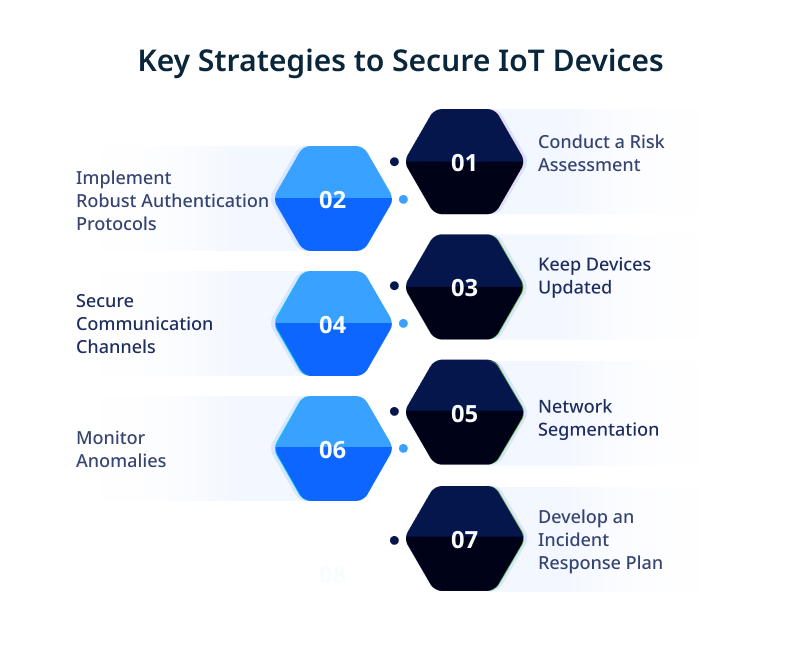
Conduct a thorough risk assessment: Identify IoT devices’ potential risks and vulnerabilities. It will help you understand the specific security measures to protect your devices and networks.
Implement robust authentication protocols: Ensure your IoT devices require strong and unique passwords or use two-factor authentication for added security. Avoid using default or easily guessable passwords.
Keep devices updated: Regularly update the firmware and software of your IoT devices to patch any security vulnerabilities. Establish a process to keep track of updates and ensure that all devices are up to date.
Secure communication channels: Use encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure data transmitted between IoT devices and other network components. It helps protect sensitive information from interception or tampering.
Segment your network: Separate your IoT devices from leading networks to contain potential breaches and limit access to critical systems. This way, even if one device is compromised, the entire network is not at risk.
Monitor for anomalies: Implement continuous monitoring and anomaly detection systems to detect any suspicious activity or abnormal behavior from IoT devices. It can help you identify potential threats early and respond quickly.
Develop an incident response plan: Have a clear plan to address any security incidents or breaches involving your IoT devices. It includes processes for investigating and containing the incident and communication and recovery strategies.
Impact of 5G on Cybersecurity
With the impending deployment of 5G networks, the impact on cybersecurity is expected to be significant. The increased speed and lower latency of 5G networks will bring numerous benefits and introduce new vulnerabilities and challenges for businesses to navigate.
First and foremost, the proliferation of IoT devices connected to 5G networks will expand the attack surface for cybercriminals. With an estimated 35 billion connected devices by 2021, the potential for cyberattacks will only increase. Businesses must secure their IoT devices to prevent unauthorized access and control.
Additionally, the high-speed nature of 5G networks opens up new possibilities for cyberattacks. The faster speeds make it easy for hackers to launch large-scale Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, overwhelming network resources and disrupting critical services.
It poses a significant threat to businesses that rely on the continuous availability of their networks.
Furthermore, the increased connectivity provided by 5G networks raises concerns about data breaches and privacy violations. With more devices connected to the network, there is a higher risk of sensitive information being compromised. Businesses must prioritize data protection and encryption to mitigate these risks.
Ways to Secure Business’s Network Infrastructure for 5G
MarketsAndMarkets report predicted that the global 5G security market will reach up to $7.2 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 41.6% during 2022-202
With the upcoming deployment of 5G networks, securing your organization’s network infrastructure is crucial to protect against the cybersecurity threats posed by IoT and 5G.
Here are some ways you can ensure the security of your network infrastructure for 5G:
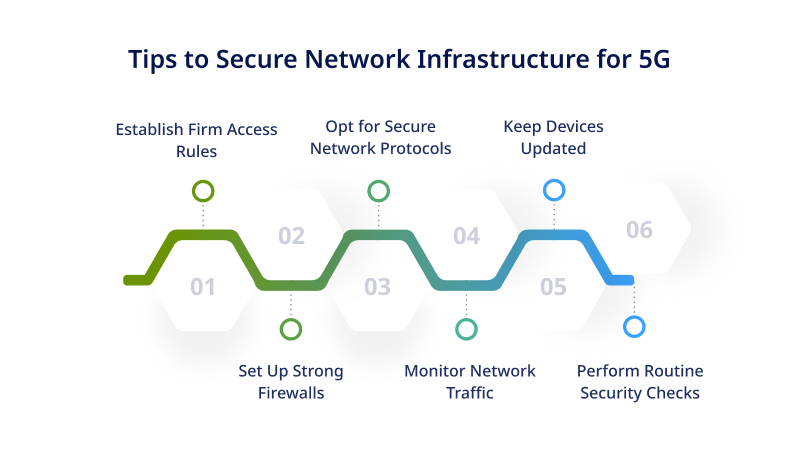
Implement Strong Access Controls
Limit access to your network infrastructure to authorized personnel only. Use strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control to ensure that only trusted individuals can access sensitive resources.
Deploy a Robust Firewall
A firewall acts as a barrier between your network and external threats. Invest in a next-generation firewall to detect and prevent advanced attacks like intrusion attempts and malware infections.
Use Secure Network Protocols
Ensure your network infrastructure uses secure protocols for data transmission, such as SSL/TLS. It encrypts the data, making it harder for cybercriminals to intercept or manipulate it.
Regularly Update & Patch your Network Devices
Keep your network devices, such as routers and switches, updated latest firmware and security patches. It helps protect against known vulnerabilities and exploits.
Monitor Network Traffic
Implement a network monitoring system that continuously monitors traffic for any suspicious activity. It lets you detect and respond to potential threats in real-time, mitigating their impact on your network infrastructure.
Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Regularly assess the security of your network infrastructure to identify any weaknesses or vulnerabilities. It can be done through penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security audits.
Adopting a Risk-based Approach to Cybersecurity
To effectively protect their networks and devices from cybersecurity threats in the era of IoT and 5G, businesses must adopt a risk-based approach to cybersecurity. It means identifying and assessing the potential risks and vulnerabilities specific to their organization and then prioritizing and allocating resources accordingly.
Here are some key considerations when adopting a risk-based approach:
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
Identify the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with your IoT devices, network infrastructure, and data. It will help you prioritize your security efforts and allocate resources effectively.
2. Establish a Risk Management Framework
Develop a framework that outlines your organization’s approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. This framework should include clear processes and procedures for managing cybersecurity risks on an ongoing basis.
3. Prioritize Risk Mitigation
Once risks have been identified and assessed, prioritize implementing security measures based on the potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. It allows you to focus resources on the most critical risks first.
4. Regularly Review & Update Your Risk Assessment
As the threat landscape evolves and vulnerabilities arise, reviewing and updating risk assessment regularly is essential. It ensures that your security measures remain adequate and relevant.
5. Continuously Monitor & Adapt
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor your network and devices for any potential vulnerabilities or breaches, and be prepared to adapt your security measures as needed.
Also Read: Top 12 Emerging IoT Technologies
Conclusion
The defense against cybersecurity threats becomes paramount. Businesses must adapt and embrace a proactive approach, fortifying their digital infrastructure with robust security measures.
Businesses can confidently navigate this transformative era by staying vigilant, regularly updating systems, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
Remember, the potential of IoT and 5G is immense, but it comes with responsibility. Being a reputable IoT application development company, let us harness the power of connectivity and stand united against the shadows that threaten to compromise it.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of IoT and 5G in the context of cybersecurity threats?
Ans:
- IoT (Internet of Things) involves connecting various devices to the internet, expanding the attack surface and increasing potential vulnerabilities.
- 5G, the fifth generation of wireless technology, enhances data speed and connectivity, yet its widespread adoption escalates the risk of cyberattacks due to the larger attack surface.
- IoT and 5G amplify the complexity of cybersecurity challenges, necessitating robust protection against a broader array of threats.
2. What are some common cybersecurity threats in IoT and 5G?
Ans: IoT Threats:
Device Vulnerabilities: Poorly secured IoT devices can be exploited as entry points.
Data Privacy Breaches: Unsecured data transmission can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Botnets: Compromised IoT devices can be harnessed for large-scale attacks.
5G Threats:
Increased Attack Surface: More connected devices and higher speeds offer more opportunities for cyberattacks.
Edge Computing Risks: Decentralized data processing can expose edge devices to vulnerabilities.
Network Slicing Vulnerabilities: Inadequately segmented network slices could lead to cross-slice attacks.
3. How are governments and organizations addressing IoT and 5G cybersecurity challenges?
Ans: IoT:
Regulations: Governments enforce data protection laws (e.g., GDPR) to safeguard IoT user data.
Industry Standards: Organizations are working on security guidelines to ensure IoT devices meet minimum security requirements.
Collaboration: Governments, manufacturers, and cybersecurity experts collaborate to share threat intelligence and best practices.
5G:
Secure Architecture: Governments push for 5G infrastructure with strong security measures embedded.
Research and Development: Organizations invest in innovative 5G cybersecurity solutions for emerging threats.
International Cooperation: Nations collaborate to set global standards and protocols for secure 5G deployment.