“Automation is cost-cutting by tightening the corners and not cutting them.”-Haresh Sippy.
Automation is the talk of the town these days. Every industry, be it medicine, automobile, manufacturing, or retail, is witnessing the impact of automation, and banking is no exception.
Yes, today, when banks have been under immense pressure and struggling with scarce resources, Robotic Process Automation has shown to be an excellent method for increasing productivity.
Today, in this blog, I will talk about the role of RPA in banking. Here, you will discover the benefits of RPA in banking, use-cases, and the process of implementing it.
I hope you are eager to know it all! So, grab a cup of coffee and something to munch on, and let’s begin.
Table of Contents
Why Go For RPA in Banking Industry?
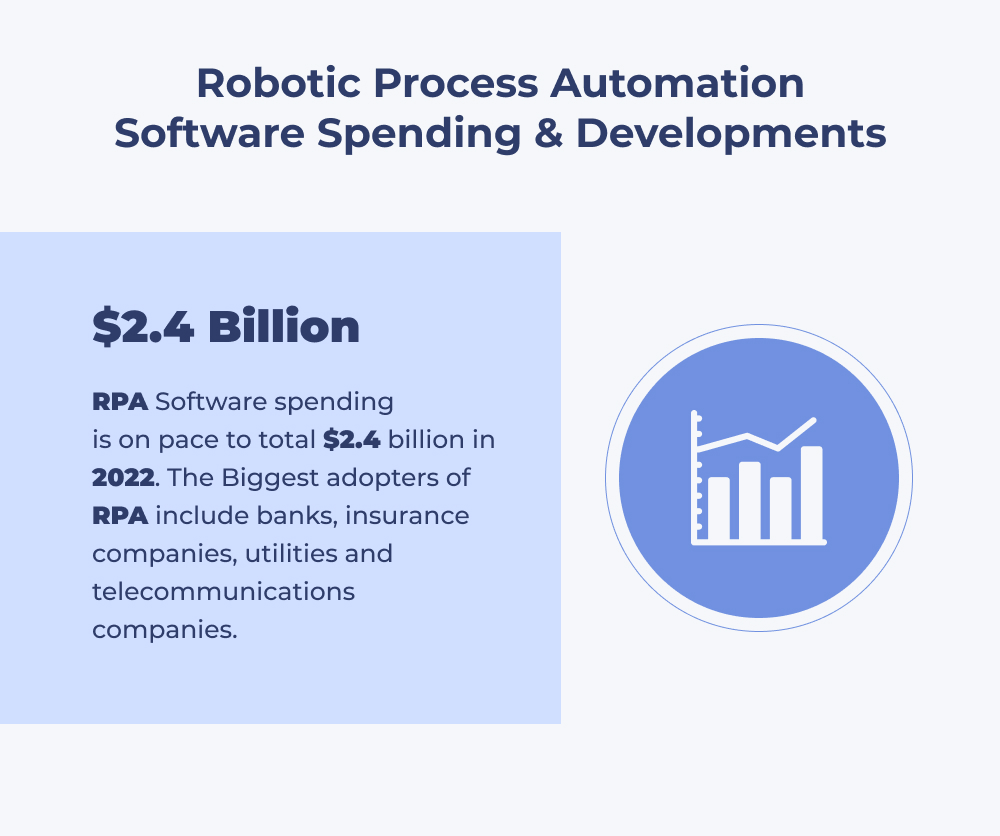
By the end of 2022, 85% of large and massive organizations will have used some form of RPA.
Banking is the ultimate relationship business, built on trust. Customers trust banks to safeguard their money and give back the interest they deserve. Banks, in turn, rely on customer loyalty for increased revenue margins and return on equity (ROE).
So what happens when the pillars of your business start shifting?
That’s what is the case now with banking!
Also Read: Digital Transformation in Banking – Everything You Should Know!
Current Challenges for the Banking Domain
- Banking revenues are under pressure as new competitors emerge. Also, technology has become an increasingly significant part of how customers interact with their banks.
- Customers today expect more than just transaction processing – they want to be engaged, understood, and looked after by their banks. And if they don’t get it, they will take their business elsewhere.
- Although customer experience can be tough to quantify, customer turnover is substantial, and loyalty quickly evolves into an endangered concept.
That’s why the banking industry today must adopt a different way to face these challenges. The best way to do this is by automating its operations using RPA tools such as UiPath.
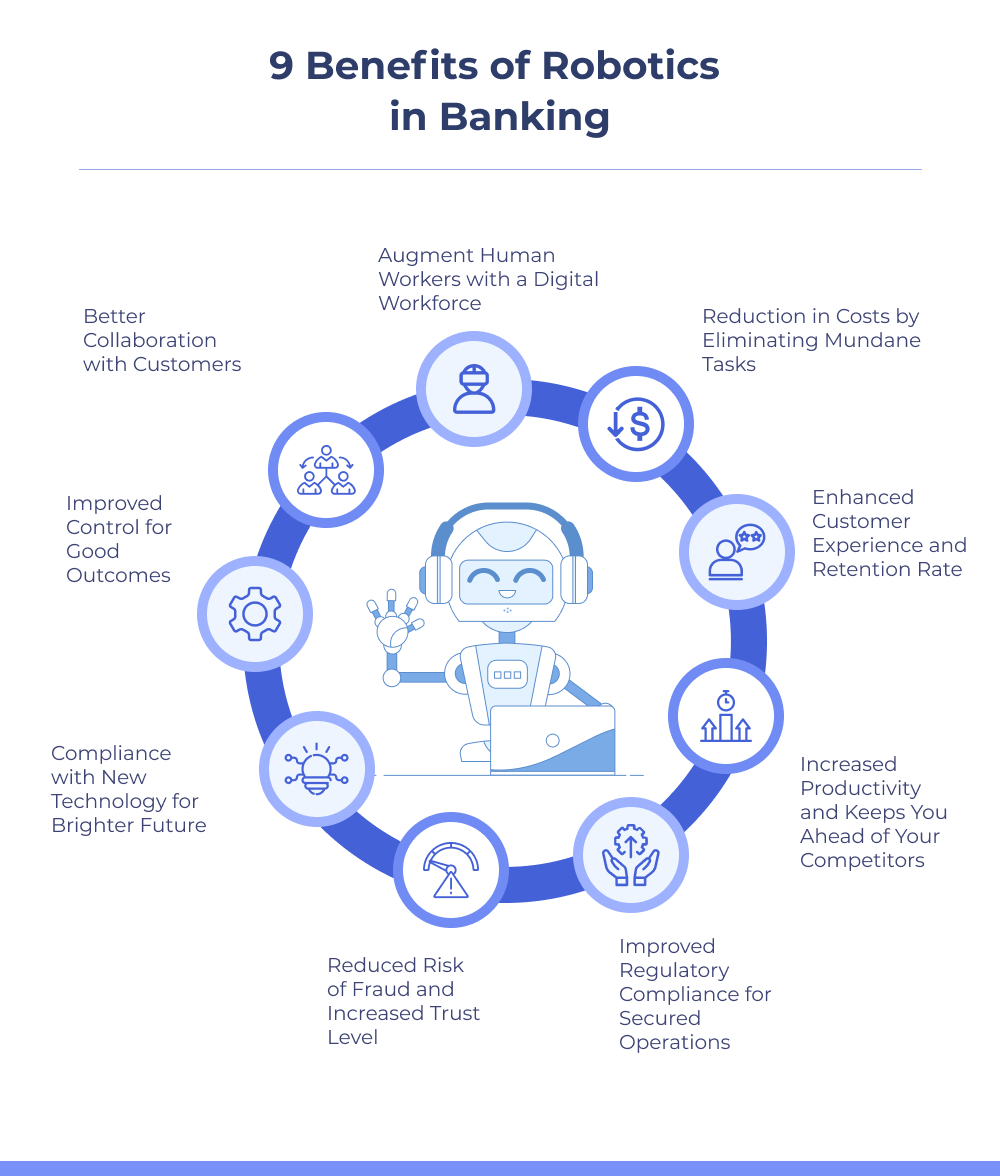
9 Benefits of RPA in Banking that are Hard to Ignore
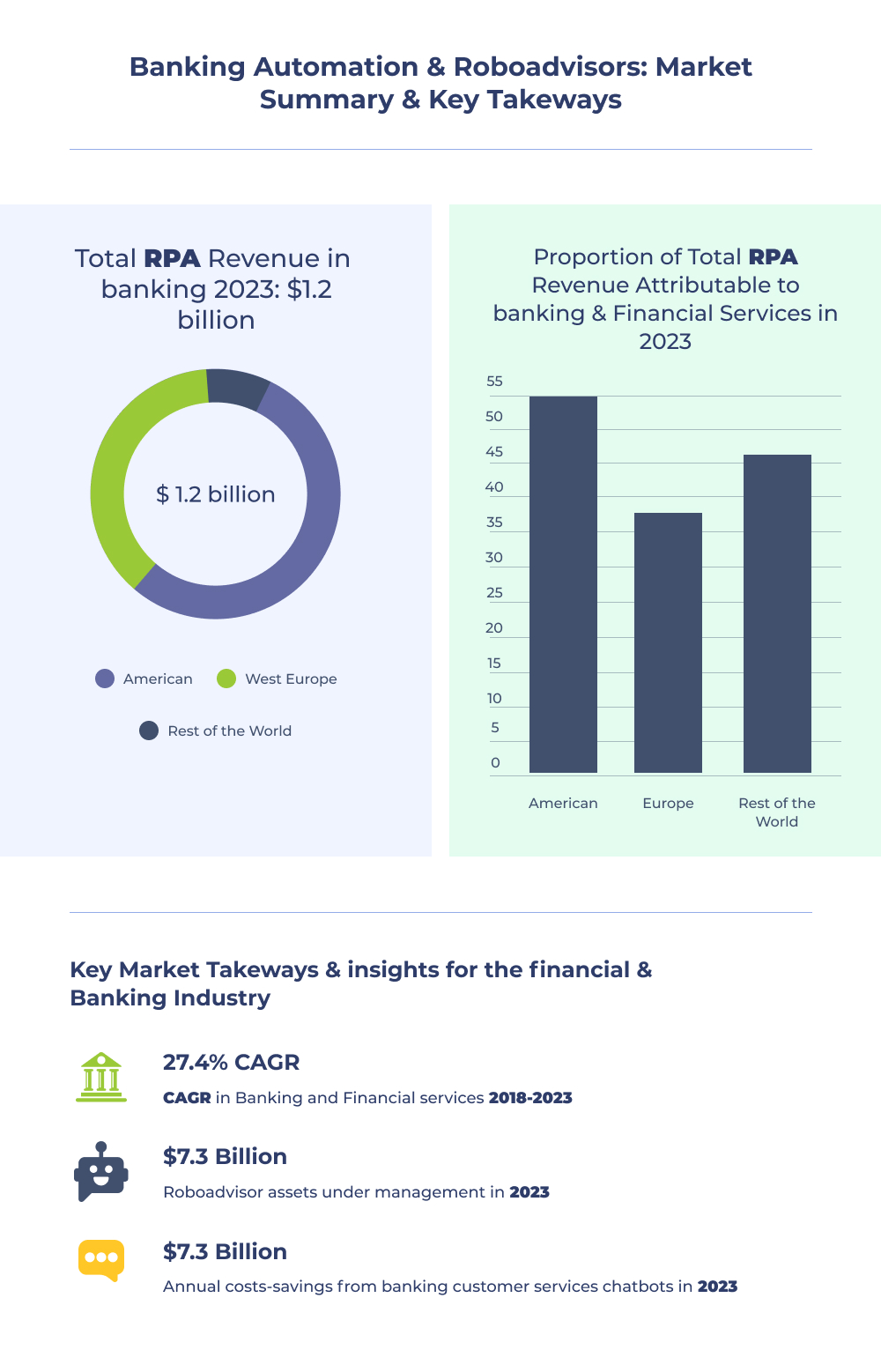
“The exponential expansion of RPA automation in banking and financial services can predict that the industry will reach $2.9B by 2022, an intense boost from $250M in 2016, as per the latest report.”
RPA can help banks provide better customer service and efficient operations and reduce the cost of processing a transaction. Here are some of its top benefits:
-
Reduction in Costs by Eliminating Mundane Tasks
RPA’s primary objective is to automate monotonous and straightforward tasks that humans usually do. Thus, freeing personnel to focus on more areas and solve complex problems. Since these bots can quickly start and close business processes quickly, banks also gain time efficiency.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience and Retention Rate
Automation of back-end operations means faster transactions, faster resolution of complaints, and increased customer satisfaction, which will drive additional revenues. Customers find it easy to do their banking with intuitive solutions that work quickly.
-
Increased Productivity and Keeps You Ahead of Your Competitors
Human employees can focus on value-added processes that add to banks’ customer experience. Also, they can concentrate on overall productivity with bots doing maximum low-level tasks. RPA tools are designed with a vision to be trained by humans without coding. Hence, they can further improve their efficiency in operations.
With RPA, banks can also add to their product lines to offer more services, including credit cards, loans, and insurance. It will allow them to drive revenue through greater profits.
-
Improved Regulatory Compliance for Secured Operations
RPA helps enforce strict compliance and security without requiring much human supervision, thus making operations more secure for customers and banks alike. Furthermore, it ensures that the various processes are being followed as set by government regulations.
-
Reduced Risk of Fraud and Increased Trust Level
Banks gain a significant advantage in risk management with RPA. The bots can detect and handle potential risks like internal fraud, credit & debit card theft, or money laundering without causing any harm to banks as well as their customers.
-
Compliance with New Technology for Brighter Future
Since financial institutions adopt new technologies that help them engage more effectively with customers, they must also comply with the regulations that determine the data handling way. RPA software ensures that only authorized people can save and access the information.
-
Improved Control for Good Outcomes
With bots handling transactions without human supervision, banks gain better control over their operations. This results in rarer blunders and a more profitable workflow for employees to manage higher-value activities, which helps banks achieve their business goals faster.
-
Better Collaboration with Customers
In most cases, customers prefer to stick with a specific banking institution because they know it best. However, assisting these customers with the bank’s range of products and services is quite challenging. RPA can help banks build a win-win relationship with customers by using the entire portfolio of services and products without any disruptions to their business processes.
-
Augment Human Workers with a Digital Workforce
RPA systems help companies to accomplish their business goals faster while keeping costs under control. It also helps companies increase collaboration between employees for better productivity and operations across the board.
10 RPA Use-Cases in Banking You Will Amaze to Know
Robotic Process Automation in banking has several use-cases, and some of the major ones are mentioned below-
1. Customer Self-Service – RPA facilitates the automation of simple, repetitive, and rules-based tasks performed by customers across various touchpoints, including ATM transactions, using digital channels like voice assistants and mobile applications.
2. Mobile Banking – Banks can use RPA to automate customer interactions through their mobile banking platforms. With this, they can provide customers with quick and context-specific information about their accounts, transfer money between accounts without requiring too much information, pay bills directly to merchants using MT103 messages, and more.
3. Fraud Detection – Banks can use RPA to process customer service calls that need complex decision-making to determine whether the call is fraudulent or genuine. This reduces the time spent on these calls and allows staff to focus more time on customer requests.
4. Cash Management – Banks can use RPA to transfer money between accounts, reconcile payments in their SWIFT environment, pay third-party invoices through MT103 messages, etc. This ensures that payment transactions are completed faster without needing any human intervention.
5. Recovering Bank Guarantees – Borrowers who do not return the bank guarantee (BG) on time need to be tracked, located, and recovered with enough proof of recovery.
This involves multiple steps that are each prone to errors with manual processing. RPA helps banks recover BG faster by leveraging technology to automate specific steps, speed up the recovery process, and improve customer satisfaction.
6. Risk Management – Banks can use RPA to help manage risks related to their products across multiple product lines with ease by automating processes that tend to be error-prone. This reduces operational costs for banks while increasing their overall efficiency.
7. Regulatory Compliance – With RPA, banks can reduce their costs by automating processes related to regulatory compliance, allowing them to ensure that they are always compliant with all regulations without requiring human intervention. This helps banks become more efficient and effective.
8. Vendor Onboarding – Banks can use RPA to automate vendor onboarding processes, which can be time-consuming and requires many manual approvals from both the bank and the vendors. This helps banks complete this process quickly and efficiently without compromising security or customer experience.
9. Vendor Management – The need for effective management of third-party vendor relationships has increased with increasing service providers. Banks can use RPA to ensure that vendors are managed efficiently with a combination of automated and manual processes.
10. Relationship Management – Using RPA, banks can improve customer experience by automating certain aspects of their relationship management process, including opening new accounts, issuing loans, and more. This ensures that customers don’t have to wait too long for their requests to be completed and allows staff to focus more time on customer service.
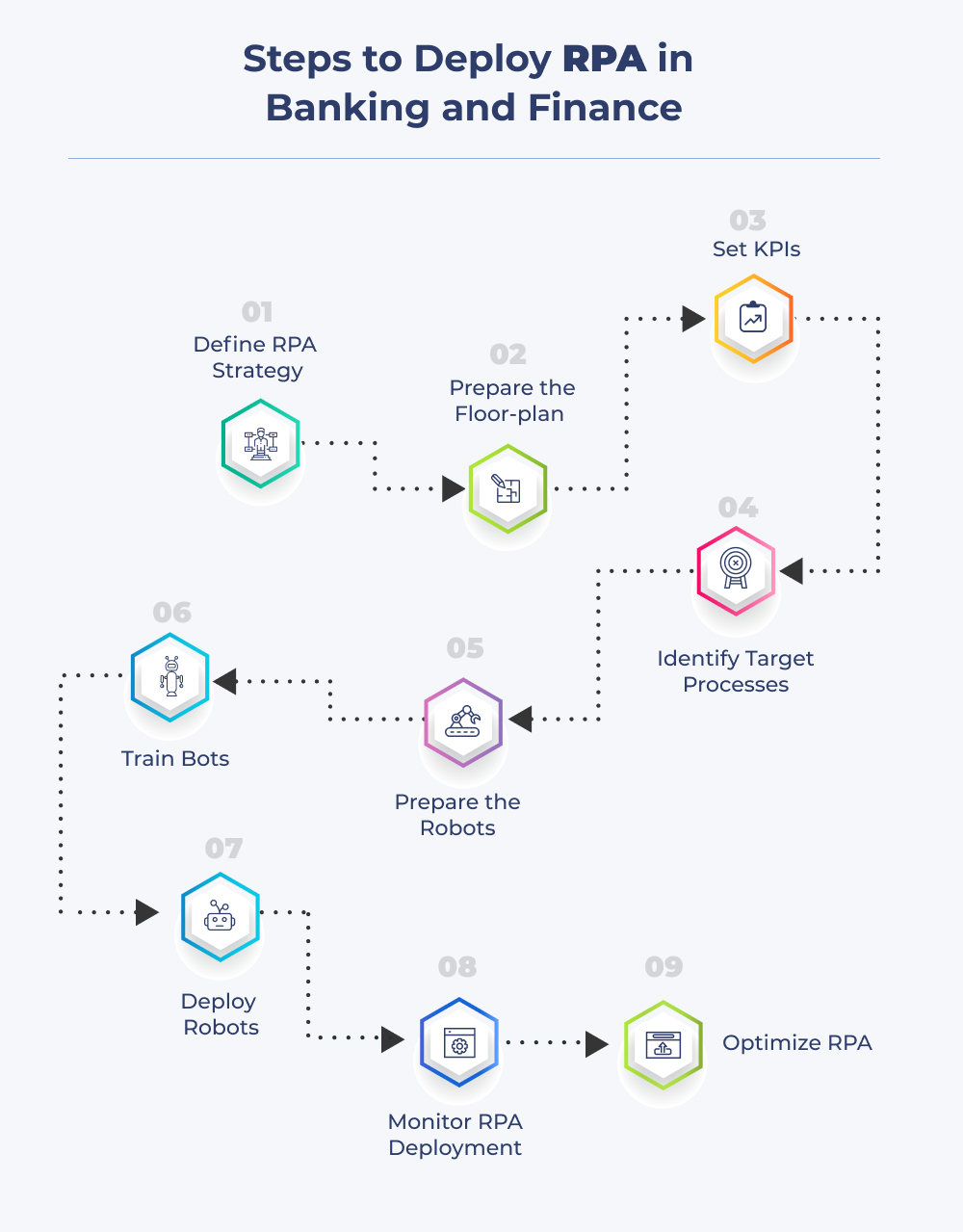
What are the Steps to Deploy RPA in Banking and Finance?
“Besides the cost and efficiency advantages, a couple of RPA’s greatest benefits are often overlooked: its ease of deployment and the speed and agility it confers on the enterprise.”– PwC White Paper
Here, I have drafted the basic steps that assist you in successful RPA implementation-
Note– You can choose a trusted machine learning development company in India for better RPA deployment in banking.
1. Define RPA Strategy
The first and foremost step is to define an RPA strategy. A defined RPA strategy clarifies how, where, and when it will be implemented. It also helps decide if there is a need for business process re-engineering or augmenting current resources with more efficient resources such as AI/ML. The strategy should include an approach to address the business problem, short and long-term goals, budgets, milestones, and timelines.
2. Prepare the Floor-plan
Preparing a floor plan for the mainframe computer and all other systems involved in the process is a must for the successful implementation of RPA. A detailed floor plan depicts the scope and extent of automation that needs to be done to ensure seamless integration between existing systems and new robots.
The floor plan should also include an extensive data mapping exercise which will enable the bots to be integrated seamlessly without causing any delay in the business process.
3. Set KPIs
After considering the strategy and floor plan, set up success metrics for your RPA implementation; these metrics should include time taken to deploy an RPA solution along with its benefits, increase in revenue generation, reduction in operational costs, and quick ROI, etc.
4. Identify Target Processes
As a part of the floor-planning process, it is vital to identify all target processes and their system dependencies. Identifying target processes in detail will help achieve higher success rates and better ROI with minimum risks involved.
It will also help identify areas where RPA doesn’t fit in or complexities due to several factors such as regulatory compliances or multiple applications.
5. Prepare the Robots
After carefully identifying all areas where RPA is required, start designing the bots, possibly one of the most critical tasks in successful automation. In this stage, it is crucial to understand how the bots will be integrated with existing systems and what type of training they require for smooth integration.
The main aim during this stage is to design a bot that can work seamlessly without any downtime or disruption in the business process.
6. Train Bots
After designing the bots, it is essential to train them thoroughly before integrating with existing systems. Training should include training the bot in an offline environment for better results and quick ROI.
It is also necessary to test the bots in a real-time environment, which will help deal with potential challenges during implementation.
7. Deploy Robots
After all, parameters are finalized, and bots are trained, it is time to integrate them with existing systems. One of the essential steps in the entire process is to thoroughly test each robot before deploying it on production systems to ensure seamless performance without any downtime or delay in the business process.
RPA life-cycle includes continuous monitoring and optimization to ensure quick ROI and a smooth transition from a manual process to a robotic one.
8. Monitor RPA Deployment
After successfully deploying the bots, it is time to monitor their overall performance using KPIs set up in the earlier stages of implementation. It is necessary that organizations clearly understand how bots are performing and take corrective actions.
Effective monitoring will help continuously optimize the bots, resulting in quick ROI and better business process outcomes.
9. Optimize RPA
Successful optimization of RPA implementation requires automated evaluation of KPIs with preset triggers, which can be activated based on organizational KPIs. This will help get the desired outcomes without affecting the existing business process flow.
Parting Thoughts
While RPA is slowly gaining traction in different industry verticals, it is necessary to understand how each business process functions and what type of challenges it has to address before taking up automation. The success of RPA will highly depend on your organization’s quality management system (QMS).
Quality should be an integral part of implementing RPA, so organizations should take appropriate steps to ensure that the entire process runs smoothly. You can even hire a banking software development company to get an excellent solution.
I hope I was able to resolve your queries regarding the role of RPA in banking! However, If you still have doubts, you can mention them in the comment section below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key risks in RPA implementation?
The key risk involved with any new technology is the lack of awareness of how it works, leading to delays or failure in implementation. Apart from this, other factors like legal compliances, data confidentiality issues, and others could affect smooth implementation.
Q2. What are the key responsibilities of an organization during RPA implementation?
The prime responsibility of any organization is to make sure that the entire process runs smoothly without affecting existing business processes. It is also essential to understand how it works, what challenges come with new technology, and whether it aligns with overall organizational goals.
Q3. What are some of the common mistakes that occur during RPA implementation?
Organizations need to take adequate steps to avoid common errors like lack of proper planning, which could lead to delays in implementation. Apart from this, organizations must evaluate their business process thoroughly before taking up automation. This will help avoid any issues during the ongoing operations.
Q4. What are some of the best practices for RPA?
Best practices for RPA include automation of only high-value tasks, creating a solid backend to support the bot process, and quick response to alerts or changes in business processes.