The Healthcare industry has evolved in the past years with new technologies and treatments to improve patient care and treatment.
According to MarketsAndMarkets, the market for cloud computing in the healthcare industry will reach $65 billion by 2025. Gartner predicted that global spending on cloud services would increase from $313 billion in 2020 to over $482 billion by the end of 2022.
With the help of cloud computing, doctors and hospitals can increase patient involvement by giving them access to their medical data, test results, and doctor’s prescription. It also makes healthcare services more accessible through telehealth.
In this blog, we will explain how cloud computing impacts the healthcare industry.
Table of Contents
Why are Healthcare Organizations Moving to the Cloud?
Healthcare providers are embracing cloud technology because it’s making healthcare more accessible to millions of patients. In the past, people could not receive care due to a lack of resources and geographical location.
With this new advancement, people all over the world are treated no matter what their condition is. Once located within one building, services are now offered from multiple locations. Patients can video chat with their doctor without ever having to leave their house. Other facilities like pharmacies are also moving towards this type of system for providing medication and treatment for their patients at an affordable price.
Despite these IT solutions, they contend with high infrastructure costs, the demand for computing resources, scalability, universal access, multi-tenancy, and increased collaboration needs. These difficulties are resolved by the following features available in the cloud:
- On-demand Service: The resources are delivered without any delay.
- Resource Pooling: Multiple users can access cloud services at the same time.
- Elasticity: It is feasible to add, delete, or upgrade depending on the company’s needs.
- Broad Network Access: A broad range of network accessibility from every location at any time.
- Measured Service: Customers are only liable to pay for their services.
Traditional vs. Cloud-Based Health Care Systems
A traditional health care system comprises hospitals, laboratories, doctor’s offices, nurses, and pharmaceutical companies that make up an interconnected network. While cloud-based health care system is online software called a cloud for storing and maintaining consumers’ health data.
Let’s look at the difference between traditional and cloud healthcare systems.
Customization: Before electronic health records allowed for customization, highly qualified programmers and IT specialists had to develop the desired bespoke solution. On the contrary, cloud-based systems are customizable with built-in functionality and care plans. As a result, many different specialized templates and simple user interfaces are available for cloud-based custom solutions.
Usage Capabilities: Traditional healthcare systems require the installation of a server, internal data storage, software, and hardware at the physician’s office. Today’s cloud-based technologies make it simple and flexible to log on from any web server-using site using any device.
Cloud services have also made collaborating, sharing data, and integrating easier. With cloud-based services, automatic upgradation and maintenance are possible, along with data access, ensuring that the information is consistent with an up-to-date version. In the conventional healthcare system, updating such information is highly difficult, time-consuming, and expensive.
Compliance and Liability: It is recommended to consider Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) rules while deciding between traditional healthcare and cloud-based healthcare services. The laws and regulations should address the need for protected health information regarding HIPPA compliance, access control, and security concerns. Care providers in cloud-based healthcare systems don’t need to be concerned about system meltdowns, natural disasters, or weather patterns, which tend to crash the systems.
The backup requirements, upgrading code-sets, security patches, and protocol requirements are unsafe and impractical in conventional healthcare systems. The cloud-based protected health information is constantly available from any location at any time. It is crucial to note that liability issues must always be HIPAA compliant.
Security: Cloud-based servers are less susceptible to malware, viruses, and hacking attempts than traditional web-based servers, although both require security awareness.
Whether you choose cloud-based or conventional healthcare solutions, the security of protected health information (PHI) is a major problem. Both systems require regular audits, analyses, and vigilance about storage capacity. Human involvement with either system is crucial because using mobile devices has raised the risks of cyber assaults on PHI.
Implementing encryption techniques with a cloud-based EHR system is still safe and more secure than conventional paper records and client/server systems. This strategy is based on how those systems are safeguarded and where they are placed.
Discover the transformative power of cloud computing in reshaping the healthcare industry. Explore its profound impact now!
Also Read: 9 Tips For A Successful Healthcare Web App Development
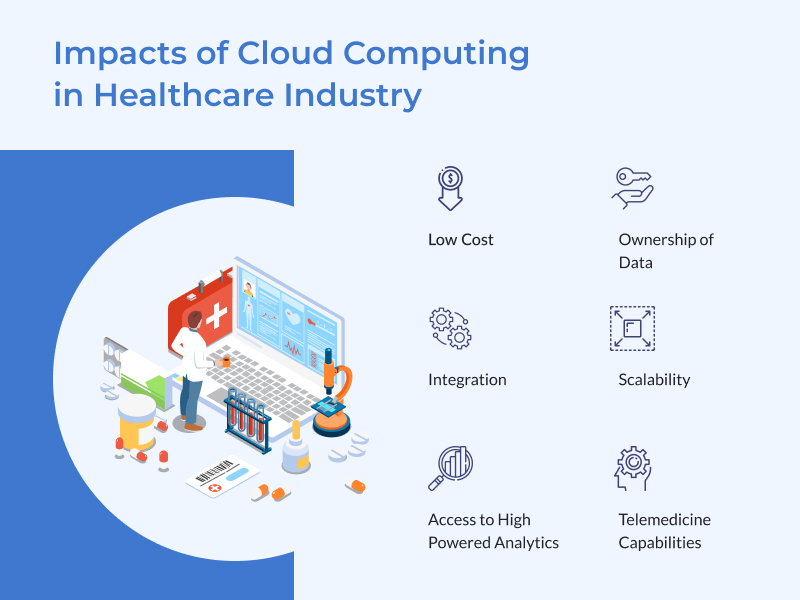
How is Cloud Computing Impacting the Healthcare Industry?
Cloud Computing impacts the Healthcare Industry in the following ways:
1. Low Cost
The fundamental tenet of cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer resources like computing power and data storage. Hospitals and other healthcare facilities are excluded from paying cash for the servers and hardware. The cost of storing data on the cloud does not come up front. You save tons of money by just paying for the resources you use.
Additionally, cloud computing offers the most ergonomic environment for scaling, which is a desirable trait in the modern era. A cloud-based environment shows to be ideal for scaling and undergoing radical upgrades while keeping the expenses in line, with patient data streaming in not just through the records in the form of EMRs but also through the abundance of healthcare apps and health wearables.
2. Integration
In the healthcare system, integration strives to create data linkages across all points of origin and storage. Patient data is easily accessible for passing and gathering insights to facilitate healthcare planning and delivery due to integration driven by cloud usage.
Healthcare professionals can now easily access patient data compiled from many sources, communicate it with key stakeholders, and issue timely prescriptions and treatment procedures thanks to cloud computing. Additionally, it reduces the distance between the experts, enabling them to analyze situations and offer their comments regardless of geographical restrictions.
The cloud-based patient data storage encourages integration between the many healthcare industry sectors, including payments, insurance, and medications. This provides for a seamless data movement between the numerous stakeholders, expediting healthcare delivery and increasing efficiency in the process.
3. Access to High Powered Analytics
Healthcare data, structured or unstructured, are both valuable. The cloud can be used to compile and perform relevant patient data computations from many sources. Big data analytics and artificial intelligence on cloud-stored patient data can advance medical research. Processing huge datasets is now more practical because of the cloud’s advanced computational capacity.
Performing analytics on medical data can also open the door to creating more individualized care plans for patients. Additionally, it ensures that when prescribing medications, nothing is forgotten, and all the necessary patient information is recorded. Hence, cloud-based data analysis is useful for locating pertinent patient data.
4. Ownership of Data
Cloud Computing makes data accessible and provides ownership to patients over their health. It increases patient participation in decisions relating to their health and promotes informed decision-making by serving as a tool for patient data education and engagement.
When storing data on the cloud, it is simple to archive and retrieves patient records and medical photographs. While cloud security remains a worry, the reliability of the cloud for data storage is higher. Data redundancy decreases as system uptime rises. Data recovery is made considerably easier because backups are automatic, and the data is kept across multiple touchpoints.
5. Telemedicine Capabilities
Accessing data remotely may be the biggest benefit of cloud storage. Integrating cloud computing with healthcare could enhance various healthcare-related processes, including telemedicine, post-hospitalization care planning, and virtual medication adherence. It also makes healthcare services more accessible through telehealth.
Apps for telemedicine improve the patient experience while bringing convenience to healthcare delivery. Cloud-based telehealth systems and applications make it simple to share medical data, increase accessibility, and give patients access to care throughout the prevention, treatment, and recovery phases.
6. Scalability
Cloud Computing provides affordable, quicker, and highly customizable scalability solutions to healthcare needs. Investing in physical storage and administration requires time and a sizable sum of money.
Cloud services can be rapidly upgraded or decreased as per business needs. Pay-as-you-go contracts can give you the flexibility of data storage for your immediate needs while also providing you with a cost estimate if you need to increase in the future.
Healthcare organizations can select the cloud platform elements they require from the pricing models and even get custom solutions.
7. Routine Administration
It is simple to streamline and update clinical and non-clinical data, financial management and planning, patient record maintenance, and appointment scheduling and monitoring on cloud platforms through IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS cloud computing models.
Additionally, cloud-based smart routing technologies and configurable IVR make it simple to manage patient assistance. The ability of cloud platforms to handle and learn from enormous data sets, combined with big data analytics, it can help with diagnosis support and speed up medical research and predictive healthcare, making it possible to store medical imaging on the cloud securely.
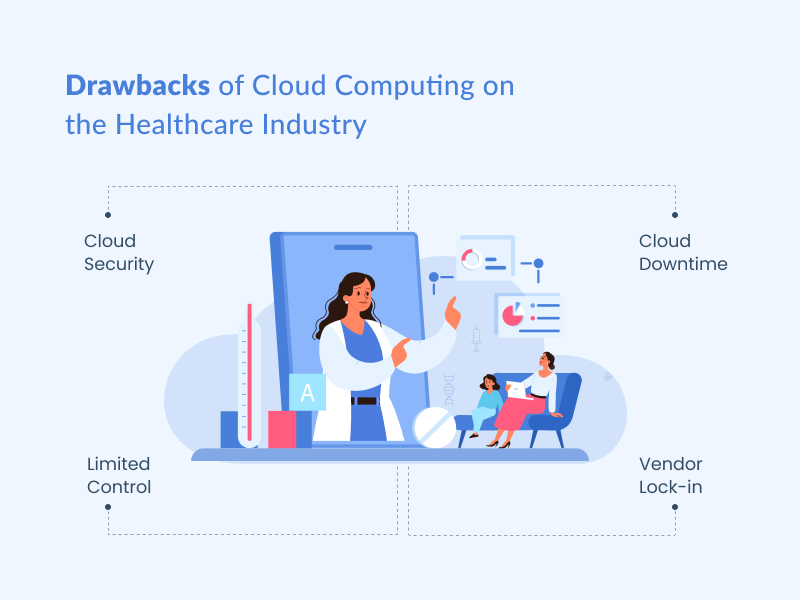
Drawbacks of Cloud Computing on the Healthcare Industry
These are a few benefits of cloud computing in the healthcare industry. However, some drawbacks must be considered when adopting this kind of technology.
Let’s discuss them below:
Cloud Security: Most cloud service providers implement appropriate security standards and industry certifications to keep their cloud environment secure. However, keeping data and files essential to your organization in virtual data centers could expose you to dangers.
Typical dangers include:
- theft or loss of data
- hijacking a service or account
- unsafe APIs and interfaces
- attacks that disrupt services
- vulnerabilities in technology, particularly in shared spaces
Various cloud service providers may achieve and maintain different data protection and security degrees. Choose your service provider carefully and ensure that the provider is stable and offers fair terms and conditions of service.
Cloud Downtime: One major drawback of the cloud is its risk of downtime. Because so much data is stored off-site, companies that rely heavily on cloud-based applications or storage are at greater risk of an outage or system failure than those with traditional setups.
One solution to this problem may be to use a backup strategy like DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service). DRaaS allows for backups of your files or programs if your system fails, giving you peace of mind without sacrificing productivity.
Limited Control: You will have minimal control over the cloud as a customer. The cloud service provider manages and monitors the cloud infrastructure. You can manage the applications, data, and services operated on the cloud. Still, you won’t normally have access to key administrative tasks, such as updating and managing firmware or accessing the server shells.
In order to remove risks, it may help to carry out a risk assessment before you hand over control to the cloud service provider.
Vendor Lock-in: The main drawback of cloud computing is vendor lock-in. Transferring an organization’s services from one vendor to another could provide challenges. Different vendors offer various platforms, and moving from one cloud to another can be challenging.
Uncover the dynamic changes fueled by cloud computing in the healthcare sector. Explore the future of medical innovation!
Examples of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry
Many top healthcare organizations have started implementing cloud computing in healthcare management procedures to provide high-quality care, reduce operating expenses, and enhance the overall administrative process.
Here are some of the most well-known cloud services for healthcare organizations.
NetApp: NetApp is a hybrid cloud data service provider. Its management platform provides clinical data in real-time, which helps operations become speedier and more effective by reducing EHR latency, hastening backup and restoration, making it simpler to accommodate growing workloads and data volumes, and streamlining data management.
Medsphere Systems: Medsphere provides various cloud-based IT solutions for healthcare organizations. The platform’s electronic health record offer services to various industries, including clinical, financial, accounting, nursing, and many more. The company also assists providers with scheduling, registration, medical records, invoicing, claims, and other tasks using Microsoft’s safe Azure cloud platform.
ClearDATA: ClearDATA’s HIPAA-compliant cloud safeguards sensitive patient data with compliance measures, devops automation, and healthcare expertise. It is built to work well with other public clouds. Additionally, the platform supports crucial apps and swiftly reacts to changes in cloud accounts by automatically detecting those changes.
Pfizer: Since 2016, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology firm Pfizer has been a pharmaceutical and biotechnology firm that has used cloud services for its projects in 2016.
As a result of its collaboration with BioNTech to create a COVID-19 vaccine, it has recently gained attention. The business recently started collaborating with Amazon Web Services to develop cloud-based solutions to enhance and speed up the production, manufacturing, and distribution procedures for clinical trial testing.
CareCloud: The open platform provided by CareCloud aids healthcare providers in increasing their efficacy and efficiency. Giving better care also enables them to interact directly with patients. Revenue cycle management, practice management, electronic health records, patient experience, mobile apps, healthcare analytics, and more applications are available.
Nintex: Nintex improves the overall patient experience by removing documents, streamlining manual tasks, and pulling crucial data out of silos. The company offers automation services to a wide range of healthcare industry experts, from doctors and nurses to manufacturers and medical devices.
Also Read: Top Benefits Of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Wrapping up
Cloud computing still has a long way to go in the healthcare industry. Its integration with quickly developing technologies like artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and the internet of medical things increases efficiency.
It creates several new opportunities for improving healthcare delivery and raises integration and resource availability while decreasing expenses.
There is no excuse not to move toward the cloud when so many advantages and strategies are in place to overcome the obstacles.
If you are looking for healthcare software development services, contact our experts.